Products
DropletSens™
Ammonium Probe
Real-time, high-frequency, lab-quality ammonium monitoring.
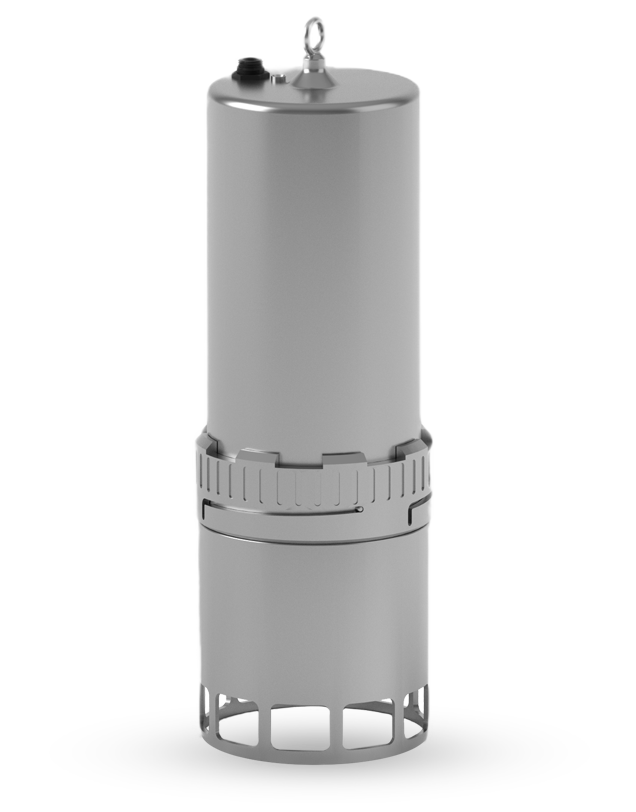
Features
- Based on established Berthelot test & indophenol chemistry
- Total Ammonia Nitrogen determined autonomously via pH mediated conversion of dissolved ammonium into ammonia
- Fully quantitative without drift
- On-device standard for performance QC
Specifications
Analytical
- Range
-
0 - 2 mg/L NH3-N (LOW)
0 - 30 mg/L NH3-N (HIGH) - Detection Limit
-
0.03 mg/L NH3-N (LOW)
0.3 mg/L NH3-N (HIGH) - Measurement Frequency
-
up to every 10 seconds
default setting is every 15 min
Operational
- Temperature range
- 0 - 35 °C
- Maximum deployment depth
- 1 m
-
Power consumption** for continuous use measuring every 15 min
- 1.5 W
Physical
- Height
- 400 mm
- Width
- 150 mm
- Weight
- 8.2 kg
Communications
- Connectivity
- RS232/RS485, Modbus, Bluetooth, SCADA compatible
- Data output
- Remote streaming
Maintenance
- Reagent change after 3 months if in continuous use
- Required inlet filter change frequency depends on application; typically 3 months for environmental applications (turbidity ≤250 NTU)
Applications
Process Control, Rivers, Streams & Lakes, Coastal, Agriculture, Aquaculture, Industrial, Environmental Monitoring, Estuary Monitoring, Catchment Monitoring, Effluent Monitoring, Nutrient Mapping, Nutrient Recovery, Nutrient Trading, Nature-Based Solutions Effectiveness Monitoring.
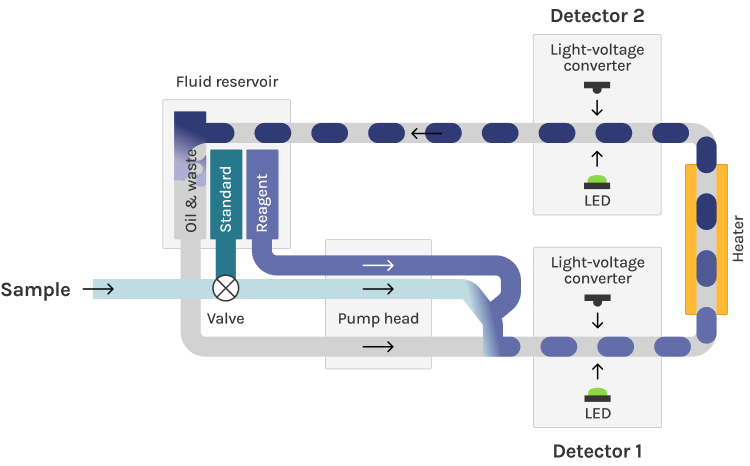
Why ammonium and/or ammonia?
Monitoring ammonium/ammonia levels is critical for optimising wastewater treatment processes and for better understanding the impact of raw sewage discharge into surface waters.
Ammonium (NH4+) and ammonia (NH3) are both part of the nitrogen cycle and exist in equilibrium. Typically harmless ammonium is prevalent (<98%) over the more toxic ammonia (<2%), unless under high pH and temperature conditions.
In wastewater treatment plants (WWTPs) ammonium is monitored for process control to ensure optimal nitrification/denitrification aimed at converting any dissolved nitrogen (NH4+, NO2, NO3) ultimately into nitrogen gas (N2↑), leaving typically low levels of dissolved nitrogen in the discharge.
However, discharge of untreated sewage during Combined Sewer Overflow (CSO) events, alongside agricultural fertiliser and industrial run-off, can result in high levels of ammonium/ammonia causing excessive algae growth and eutrophication in rivers, estuaries and coastal waters, with damaging effect on local aquatic life.
Incoming Environment Act 2021, Section 82 legislation in the UK will require operators to monitor ammonia levels up and down-stream of all WWTPs and CSOs, which equates to >50,000 locations.


Monitoring Solutions
We offer the following solutions for monitoring ammonium:
A. SWS turn-key solution: fully autonomous SWS sensor probes with own battery, connectivity and user interface:

B. Third party static, floatable & moveable integrated solutions.
- B1. SWS sensor probes integrated into WATR's hybrid bankside installations
- B2. SWS sensor probes mounted onto WATR's Pro 2.0 floatable platform
- B3. SWS sensor probes mounted onto CCI's WADR moveable platform - coming soon - notify me


